Methylsulfonylmethane (MSM) is a form of organic sulphur that acts as a building block for hair's main protein: keratin. Research shows that MSM helps to thicken the hair and can provide more shine. There are many indications that MSM has many positive effects. From analgesic, anti-inflammatory to acceleration of wound healing. This makes MSM a popular supplement with many positive claims behind its name. But what is true and does it really do so much good for the hair and body?
Table of content:
- What is MSM?
- Expected results of MSM
- How and from what is MSM made?
- Expected results of MSM powder for hair
- Possible side effects when using MSM powder
- How do you use MSM?
What is MSM?
Methylsulfonylmethane is an organic sulphur compound that occurs naturally in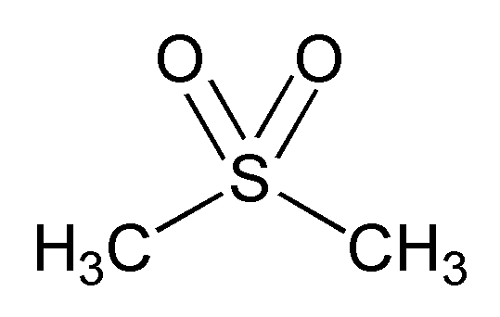 plants, animals and humans. MSM is closely related to dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO), an organic compound known in medicine as being miscible with a large number of organic solvents. As a result, it is rapidly absorbed into the skin and body. MSM also has these properties, as a derivative of DMSO, and makes it popular because it can quickly penetrate deep into the skin without damaging it. This allows it to carry other compounds and makes it a popular painkiller without unpleasant side effects.
plants, animals and humans. MSM is closely related to dimethylsulphoxide (DMSO), an organic compound known in medicine as being miscible with a large number of organic solvents. As a result, it is rapidly absorbed into the skin and body. MSM also has these properties, as a derivative of DMSO, and makes it popular because it can quickly penetrate deep into the skin without damaging it. This allows it to carry other compounds and makes it a popular painkiller without unpleasant side effects.
Expected results of MSM
The analgesic effect of MSM has been established by research for the treatment of rheumatic complaints such as osteoarthritis. In a study of people with osteoarthritis of the knee, it was found that those who took MSM powder daily had less pain and more movement in their knees.
View the study here: Efficacy of methylsulfonylmethane supplementation on osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomised controlled study.
Another study showed that MSM intake had a relieving effect on a group of healthy young, but untrained, men who performed intensive exercise. Daily intake of MSM for 10 days had a relieving effect on oxidative stress occurring after an intense work out. Untrained people who do not exercise or exert themselves frequently are at risk of producing more free radicals. Exercising logically goes hand in hand with an increase in your energy consumption and thus increased oxygen burning. This causes you to produce more of these free radicals. The free radicals can cause muscle fatigue, muscle damage and inflammation. The men in the study who took MSM daily had fewer problems with this.
How and from what is MSM made?
It occurs naturally in fresh, unprocessed and uncooked food, especially in raw fish and meat. When preparing food, a lot of MSM is lost through heating and other processing, so absorption through food is often poor. MSM, as 'organic sulphur', is much easier for the body to absorb than the mineral sulphur. The synthetically produced MSM powder therefore makes it possible to take MSM without having to ingest unrealistic amounts of food. However, there are good natural sources of MSM such as fruit, vegetables, cereals, beer, port and cow's milk.
Expected results of MSM powder for hair
Hair consists of approximately 95% keratin. The natural sulphur MSM promotes the transfer of keratin because it easily penetrates the connective tissues and supports the bonds that keep hair strong and healthy. In addition, it supports the growth phase of the hair follicles. Sulphur itself is an important component of connective tissues such as cartilage and skin. It also ensures that the skin remains supple and strong. The concentrated natural sulphur compound MSM is an easy way to get a lot of it. It also makes MSM a potential complement to other hair loss remedies such as minoxidil and finasteride. It penetrates the skin quickly and can therefore help to bring important substances to hard-to-reach places in the body. What is important to note here is that research has not shown that MSM addresses the causes of hereditary hair loss.
In addition to its analgesic effect, MSM has good properties that correspond to factors that can prevent hair loss. It can therefore potentially improve hair condition in people with autoimmune forms of hair loss. The anti-inflammatory effect is important for improving alopecia areata and telogen effluvium.
Research has also shown that MSM improves the hair's shine. Test subjects saw that a daily intake of as little as 1 gram improved hair lustre. It also significantly increased their hair volume after 8 weeks of use. A dose of 3 grams per day seemed to be the most effective. Although the exact effect is not fully understood, the hypothesis is that MSM releases the sulphur to keratin, which helps to strengthen the bonds between keratin molecules in the hair and nails.
In another study on the effects of MSM on the skin, a significant improvement of the skin was also demonstrated. It reduced visible wrinkles and improved overall skin health.
See the studies here:
- Beneficial Effects of a Sulfur-Containing Supplement on Hair and Nail Condition
- Effects of Oral Supplementation With Methylsulfonylmethane on Skin Health and Wrinkle Reduction
Possible side effects when using MSM powder
During the first period of use, MSM can have a slightly laxative effect, as the body has to get used to taking the powder. In addition, MSM has a somewhat bitter taste. To improve the taste, dissolving it in (fruit) juice or lemonade is recommended.
How do you use MSM?
Take 1-4 teaspoons (4-16 grams) daily by dissolving the MSM powder in (fruit) juice or water and drink it. MSM powder combines well with other food supplements. MSM is suitable for anyone who wants to supplement the daily diet.